what symbol can you use to run a command in the background?
SSH (Secure Shell) is the end to end encrypted networking organization that allows users to get access remotely from client to server or arrangement. Because of its disproportionate cryptography security system, it's pretty much safety and secure to access the server even from an unsafe customer network. But sometimes due to inactivity or bad network signal, SSH remote access can get disconnected. Whatsoever the reason is, every bit a Linux administrator, it's a vital job to continue SSH sessions and processes running after disconnection.
Reasons Why SSH Sessions Get Disconnected
In a nutshell, SSH tunnel proxy error, network timeout, using the wrong network port, or even not logged into your system as root user tin can also get yous disconnected from the SSH remote administration. In this mail service, we are going to discuss the nigh often asked question about SSH; how to keep SSH sessions and processes running afterwards disconnection is occurred.
1. Continue Running SSH Sessions Using the screen Command
The screen command is the most used and useful command for SSH administration. The screen control can resolve hostname problems for both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. With root functionalities, the screen control can log out or dismiss a session from the client cease to the server stop. If you're a very newbie at Linux SSH, here are some CLI that can assistance you to install and find manuals of the screen command.
For Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt install screen
For OpenSUSE:
$ sudo zypper install screen
For Arch Linux:
$ sudo pacman -South screen
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
$ sudo yum install screen
Afterward you're done installing, kickoff monitoring your system start screen.
$ screen $ screen --aid
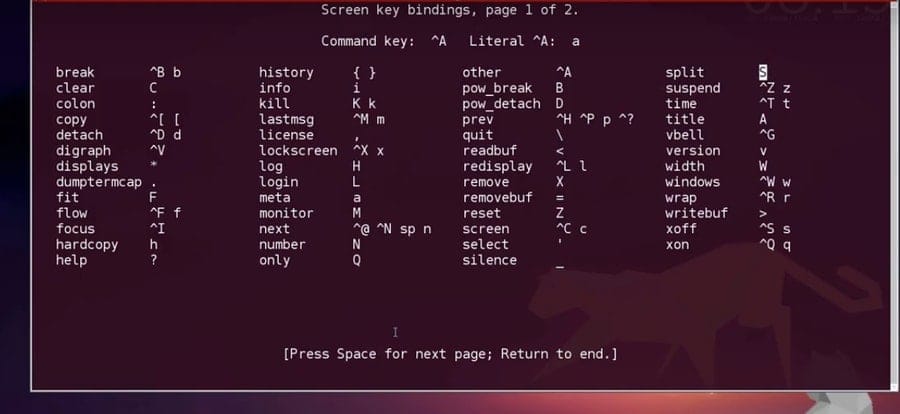
One time you accept the admission, SSH into the server, you desire to get admission remotely. If you lot're planning a long night work from your station, but you don't desire to become your SSH client downwards, yous can use the screen command. This tin detach your screen session, but no worries, the tasks you initiated will be completed.
To detach your screen press Ctrl-A and then Ctrl-D from your keyboard. You can log in to monitor the piece of work progress anytime from your last. To re-connect or connect with the existing i with the session, use the following CLI.
$ screen -r screen -D -r
ii. Go on Running SSH Sessions Using the tmux Tool
The tmux or final multiplexer is a very popular and useful tool for programmers and system administrators that allows users to switch betwixt program to program in the same concluding. To continue SSH sessions running in the background, tmux tin exist a very quick solution. It can detach and reattach applications where the processes are kept running in the background. Here is the installation instruction of tmux for Linux distros.
For Curvation Linux:
$ sudo pacman -S tmux
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
$ sudo yum install tmux
For Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt-get install tmux
For OpenSUSE:
$ sudo zypper install tmux
After installing tmux, get-go the tmux session using terminal commands. It won't take much time to become installed. One time you've done installing you tin can at present go started with tmux. To outset tmux, but type tmux in the last.
$ tmux
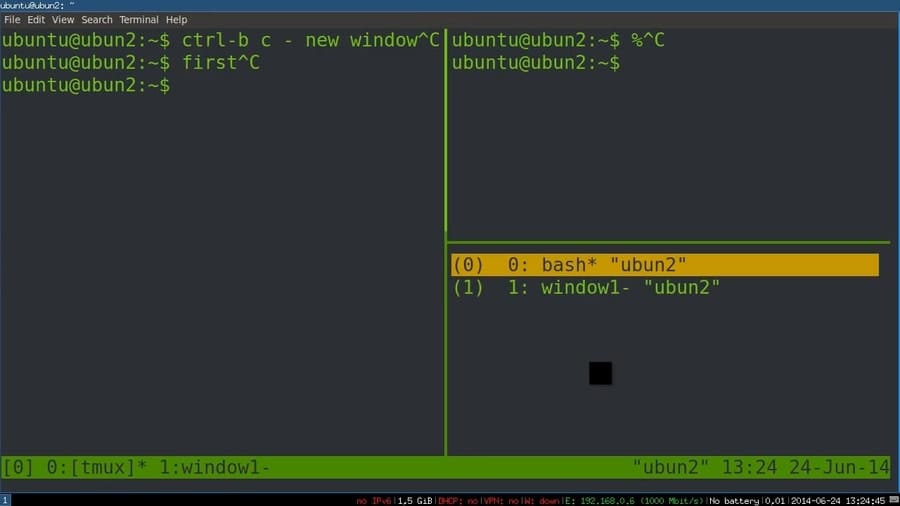
If you lot need to run more than one terminal multiplexer to keep all SSH sessions running in the background, in that case, y'all may discover difficulties to switch between tmux to tmux. Here are the command lines to switch 1 form another.
$ tmux disassemble $ tmux attach $ tmux attach -t 2
To bank check all the tmux screen use the tmux list command.
$ tmux ls
3. Proceed Running SSH Sessions Using the byobu Tool
The byobu tool is mostly used for remote SSH administration and on-screen monitoring on Linux. It is an open source-sourced software and can exist used alongside the tmux or the screen tool. You tin meet the current status, notifications, and letters with the byobu tool. Though the byobu comes installed by default with Ubuntu. But if it doesn't, yous can install it inside your Linux automobile. To cheque whether byobu is installed or not in your system by checking the other versions of byobu.
$ byobu --version
Then enable byobu, it will help to go on your SSH sessions running in the background subsequently even disconnection.
$ byobu-enable
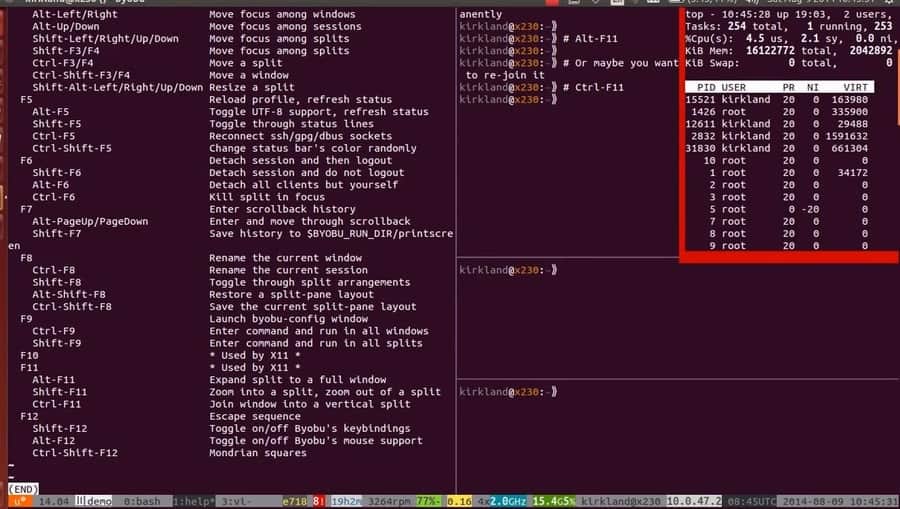
Here the installation processes are explained with CLI.
For Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt install byobu
For OpenSUSE:
$ sudo zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/utilities/openSUSE_Leap_42.iii/utilities.repo
$ sudo zypper refresh $ sudo zypper install byobu
For Arch Linux:
$ yaourt -S byobu $ packer -Due south byobu
For Ruby-red Hat Enterprise Linux:
$ sudo yum install byobu
For Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install byobu
To get started with byobu, simply type byobu in the terminal and hit Enter.
$ byobu
Now, if yous're using the tmux or the screen, you tin can choose and select betwixt any of them for backend collaborated.
$ byobu-select-backend
Now, yous can manage and continue your SSH sessions running in the background after disconnection, utilize the system keyboard function keys. To get started with SSH aslope byobu, press CTRL+SHIFT+F2 from your keyboard to enable the SSH environment. To move your SSH sessions forward and backward you can use ALT+UP and ALT+Downwards.
To disconnect your SSH sessions press F6 from the keyboard. Now, if you're looking for detaching just not disconnect the session, hither yous get. To disassemble SSH sessions and still get connected, press SHIFT+F6. Here is one more actress keyboard control for you. To keep only current the screen session active and close all other windows press ALT+F6.
four. Keep Running SSH Sessions Using the nohup Command
The nohup or 'no hangup' command is a very useful alternative tool for the screen or the tmux. It also allows users to keep the SSH sessions running fifty-fifty later they got disconnected. The nohup command tells the arrangement to run all processes in the background by avoiding the point hang up (SIGHUP).
To check the nohup manuals and options form your Linux last, type the following command in the terminal and hitting Enter.
$ nohup options
To check the currently active job lists, use the -l command from your last.
$ jobs -50
Now, for SSH connectedness, to avoid connection lost and keep your sessions running afterwards disconnection, employ the nohup command lines following by your job. You can also get the output list of your jobs in a text file by using the cat control alongside the nohup command.
$ nohup ./hello.sh $ true cat nohup.out
To run a process in the background, you can use the & symbol simply later the nohup command. Like, if I desire to test ping for wordpress-408970-1286763.cloudwaysapps.com in the background, the command line volition exist just similar the following line beneath. And when you think your chore is done, to see the outcome, use the pgrep command.
$ nohup ping world wide web.ubuntupit.com & $ pgrep -a ping
5. Keep Running SSH Sessions Using the disown Command
If y'all don't have the system root privileges, maybe this one is going to solve your trouble. The disown control tin can make any task unlisted from your running system log. Thus, information technology tin can hide an undergoing process to avoid all the auto log out errors or the s ignal hang upward (SIGHUP). You tin actually use the diswon procedure management command to keep your SSH sessions running by hiding your chore.
To remove or hide your task from the task manager, use the diswon command in the terminal.
$ disown <task>
To check the electric current status of the task, use the current crush control.
$ current shell
Y'all can also gear up a list of tasks at a single line final control.
$ disown jobs1 $ disown jobs1 jobs2 ... jobsn
And to check the task list, use the -l command.
$ jobs -50
To remove all current jobs from the window, type the -a syntax following by the disown command.
$ disown -a
To remove just one or the running job from the window, utilise the -r syntax following past the diswon command.
$ disown -r
Now for SSH, to run a job in the background after the session is connected, use the -h syntax. This process can continue your SSH sessions running even after disconnection.
$ disown -h jobID $ disown -h %2
Fixing the timeout Error of SSH in RHEL
When you're continued to the SSH on Red Lid Enterprise Linux (RHEL), y'all may get a frequent timeout problem and get your connection lost. This problem occurs due to the invalid response time form either the client end or the host end. In your Red Hat root directory, you have to find and edit the sshd_config.txt file to solve these timeout trouble. In one case y'all're done, y'all can get your SSH connexion dorsum fifty-fifty after getting asunder.
There within the sshd_config.txt, file you will find 2 options named as ClientAliveInterval and ClientAliveCountMax, yous demand to edit these log files to maximize the server to client response fourth dimension. The timeout interval is calculated by multiplying the values of ClientAliveInterval and ClientAliveCountMax.
All you need is to edit the time duration of this 2 values according to your arrangement and network responding duration. Allow you want to maximize the fourth dimension x minutes for the client interval stop and 5 times for the client count, so your text registry within the sshd_config.txt file will be similar beneath. And then, restart the SSH.
ClientAliveInterval 10m ClientAliveCountMax five
Final Thoughts
For a system administrator, proceed SSH sessions and processes running is a crucial chore to satisfy the client and to fulfill the task. Getting disconnected and frequent sessions lost is very much annoying and bothersome. So in this post, nosotros have tried to discuss and illustrate the reasons why SSH sessions get disconnected and as well described all the possible methods on how to keep SSH sessions running afterwards disconnection.
If you have ever gone through the hassle of SSH session disconnection and know how abrasive it could be, please share your experience with us. And also practice comment if you have anything to add or ask anything related to this post in the annotate department. Don't forget to share this post with your friends on social media.
banvarddonentolon.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.ubuntupit.com/how-to-keep-remote-ssh-sessions-running-after-disconnection/